Change SSH Connection Port
This process will guide you through changing the default SSH port 22 to a custom port for increased node security.
Overview
SSH (Secure Shell Protocol) is the standard protocol used to gain remote access to computer systems (servers) for administration purposes. In our case, it's applicable mostly to VPS (Virtual Private Server) systems in the cloud.
Utilizing TCP/IP (Transfer Control Protocol/Internet Protocol), a default connection is made via the widely known port 22. This encrypted connection is established between the computer and server operator, from the local end of the connection (via terminal or bastion host) to the remote server. SSH Key Pairs are used to authenticate and provide the encryption/decryption mechanisms.
Centralized
In centralized infrastructure where there is a centralized security setup, it is easier to keep a well-known port in place. In order to gain access to the centralized network, you must traverse several layers of security before you are able to access these internal servers.
Decentralized
In decentralized scenarios such as Constellation's Hypergraph network, the same level of centralized security is typically not obtainable. Instead, access to VPS systems are direct. This opens up vulnerability to nefarious actors from DoS (Denial of Service) attacks to unauthorized access attempts.
Guidelines
Security
The custom port is a preventative measure to add more ambiguity to our VPS security, but offers no additional protection beyond that. It's important to keep a watchful eye over your validator node to ensure it is secure and running properly.
Custom port selection
This guide uses port 2222 as an example, but the node operator must select their own custom port (between 1025—7999 or 10000—65535) to configure.
Ports 8000-9999 may be reserved for metagraphs and Global Layer 0, therefore that usage range is discouraged.
Configuration
Before you Begin
Make sure you have your p12 private keystore backed up before you continue this procedure!
See documentation to backup your p12 for Macintosh or Windows.
VPS Firewall Settings
Reminder
Port 2222 is used as an example; please select another custom port for your own configuration.
Allow port 2222 in your VPS firewall settings
Log into your VPS provider admin console and add a new rule allowing inbound connections to port 2222, restricting access only to the local IP.
The firewall should contain an existing entry for SSH access on port 22. Do NOT delete the existing port 22 rule at this time. Copy this rule by adding custom port 2222. In the example, 113.113.113.113/32 is the local IP.
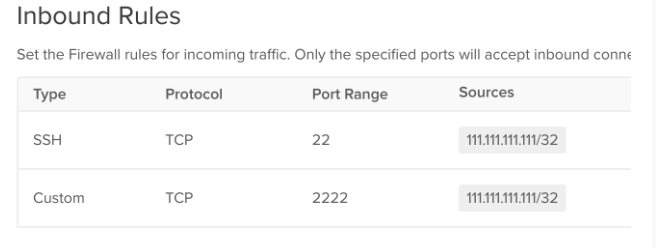 Example shows Digital Ocean
Example shows Digital Ocean
SSH daemon config
Access your VPS node in order to update the sshd_config file. This is the default global configuration file for Debian OS.
Windows
Windows should use a terminal emulator such as PuTTy.
Mac
ssh -i <your_identify_file> nodeadmin@<your_ip_address>
From your VPS, we will access the sshd_config with sudo (super user).
sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Navigate to the line where you see #Port 22, using the arrows on your keyboard.

If there is a # symbol (or comment) in front of Port 22, remove the # and replace the value 22 with a port number of your choice between 1025—7999 or 10,000—65535.
Let’s take the example 2222.

On your keyboard, press ctrlo.
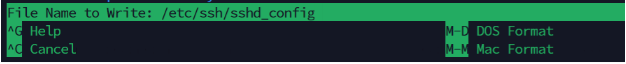 👆🏽 You should see this message at the bottom of the screen.
👆🏽 You should see this message at the bottom of the screen.
Hit Enter to confirm, then press ctrlx to close the text editor and return to command prompt.
Confirm
With the following command below, we should see our updated Port 2222 echoed to the screen.
sudo cat /etc/ssh/sshd_config | grep "Port 2222"
If you do not see Port 2222 echoed to the screen, replace 2222 with your port number and repeat the steps above.
Restart
Restart the SSH service:
sudo service sshd restart
Before Testing and Confirming
IMPORTANT
Do not close your current terminal session! In the event that something goes wrong, you will lose access to your VPS.
( Again make sure you have our p12 file backed up before continuing )
Keeping the current session open will allow you maintain your current connection, until you verified you are up and running!
On Windows: PuTTy config
Update your terminal session configuration.
Since your SSH port has changed, the connection cannot be established any longer using port 22. The SSH client needs to be updated to use your new port instead.
In PuTTy, load your TestNet profile configuration. Enter 2222 in the Port field.
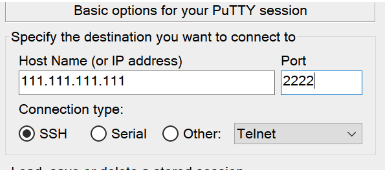
Makes sure to save the new profile settings to your TestNet configuration, and test your connection with the updated port.
On Mac: Terminal
The old command used to connect to your VPS node using the standard SSH port 22 looked like this:
ssh -i ~/.ssh/cn-node-id nodeadmin@113.113.113.113
With this new command, specify your custom port to replace 2222.
ssh -p 2222 -i ~/.ssh/cn-node-id nodeadmin@113.113.113.113
Delete old SSH rule
Now that you have tested and successfully accessed your VPS node with your custom port, log into your VPS and delete the original port 22 SSH rule from the firewall settings.

Done!